在这里记录自己的嵌入式学习方向和成果,只做大方向的规划,目前学习规划如下:
√ linux基础学习
√ arm裸机开发(使用正点原子IMX6ULL的板子)
√ linux的系统移植
√ Linux核心驱动开发
√ qt
√ linux c 应用编程
linux 显示驱动学习:
- 手动写寄存器来点亮一个屏
- 对接上层框架
在现代多核处理器系统中,处理器核心的组织方式和任务分配策略直接影响系统的软件设计与通信方式。按照核心间的共享程度,多核系统通常可以分为 对称多处理(SMP, Symmetric Multi-Processing) 和 非对称多处理(AMP, Asymmetric Multi-Processing) 两类。
SMP 系统中的所有核心平等地共享同一份内存和 I/O 资源。每个核心运行相同的操作系统实例,一个核通过_start初始化以后,唤醒其他的核做secondary_start_kernel,可以执行任意任务,并通过统一的调度器协调任务执行。
AMP 系统中,各个核心独立运行自己的操作系统实例或裸机程序,它们之间可能不共享内存,甚至运行不同类型的操作系统。典型应用包括 异构多核 SoC,如 Cortex-A 与 Cortex-M 核组合,或者 CPU 与 DSP 的混合系统。
| 特性 | SMP | AMP |
|---|---|---|
| 核心对等性 | 所有核心对等 | 核心独立 |
| 操作系统 | 单实例,多核心共享 | 每核心独立操作系统 |
| 内存访问 | 全部共享 | 部分共享或不共享 |
| 通信方式 | 共享内存 + IPI 中断 | 消息通道(RPMsg / Mailbox) |
| 通信目标 | 任务同步、调度、资源管理 | 命令下发、事件通知、数据传输 |
调度应用
场景:当一个 CPU 修改了任务优先级 / 唤醒了一个任务,但该任务更适合在另一个 CPU 上执行时。
做法:当前 CPU 向目标 CPU 发送 IPI,目标 CPU 立即触发调度器,切换到这个任务
跨核函数调用(smp_call_function)
场景:某个内核子系统需要在所有 CPU 上执行一段代码,比如linux下的fiq-debugger机制:当某个核卡死的时候依然可以通过smp_call_function让该卡死的核执行传入的回调函数,在调试的时候非常好用,比如我的代码导致了某一个核卡死了,可以通过smp_call_function的机制让卡死的核dump一些信息
做法:一个 CPU 发 IPI 给其他 CPU,让它们都执行一个回调函数。
核间通知 / 快速消息传递
在linux下多个a核间的通讯相对来说比较简单,主要是通过向需要通讯的核发一个ipi中断来实现,ipi中断以及中断处理函数在初始化的时候进行注册
分析前先看下面这个函数:
1 | .macro get_phy, reg, symbol |
adrp \reg, \symbol 计算symbol相较于pc寄存器的页基地址,可以看成:
1 | reg = (symbol & ~(0xFFF)) - (pc & ~(0xFFF)) + (pc & ~(0xFFF)) |
再通过add \reg, \reg, #:lo12:\symbol将symbol的低12位与reg相加存放回reg中
这么使用是为了解除直接使用ldr reg,=symbol的限制
首先从内核的入口_start进行分析:
pbuf 结构体:
1 | struct pbuf { |
armv8中,执行发生在4个异常级别之一,在aarch64中,异常级别决定了特权级别,类似于armv7中定义的特权级别,异常级别决定特权级别,因此在Eln执行对于特权Pln。类似地,具有比另一个更大的n值的异常级别处于更高的异常级别,一个数字比另一个小的异常级别被描述为处于较低的异常级别。
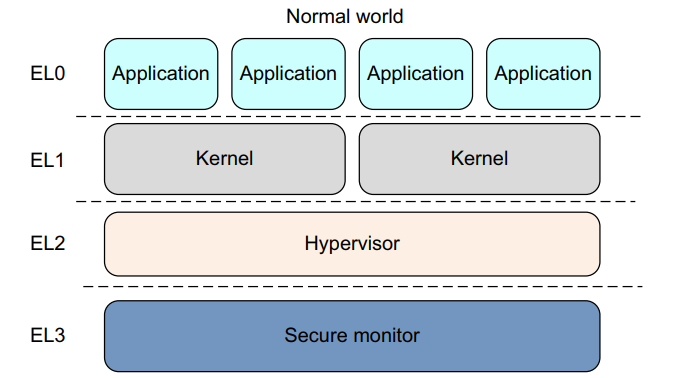
Linux驱动开发和裸机开发的区别**
Uboot是一个裸机程序,比较复杂,就是一个bootloader。作用就是用于启动Linux或其他系统,Uboot最主要的工作就是初始化DDR(Linux的运行是运行在DDR里面的),一般linux镜像zimage(uimage)+设备树(.dtb)存放在SD,EMMC,NAND,SPI FLASH等等外置存储区域。
Rgb 三原色组成每个像素点,而分辨率就是像素点的个数,而argb则是增加了透明通道,
缺失模块。
1、请确保node版本大于6.2
2、在博客根目录(注意不是yilia根目录)执行以下命令:
npm i hexo-generator-json-content --save
3、在根目录_config.yml里添加配置:
jsonContent:
meta: false
pages: false
posts:
title: true
date: true
path: true
text: false
raw: false
content: false
slug: false
updated: false
comments: false
link: false
permalink: false
excerpt: false
categories: false
tags: true
